E
cosystem
servicesdelivered
Provisioning
Regulation & maintenance
Cultural
Abiotic
C
ontribution
topolicyobjectives
Water Framework Directive
Floods Directive
Birds & Habitats Directive
2020 Biodiversity Strategy
P
otential
biophysicaleffects
Runoff
Reducing pollution
Soil conservation
Habitat
Climate Change
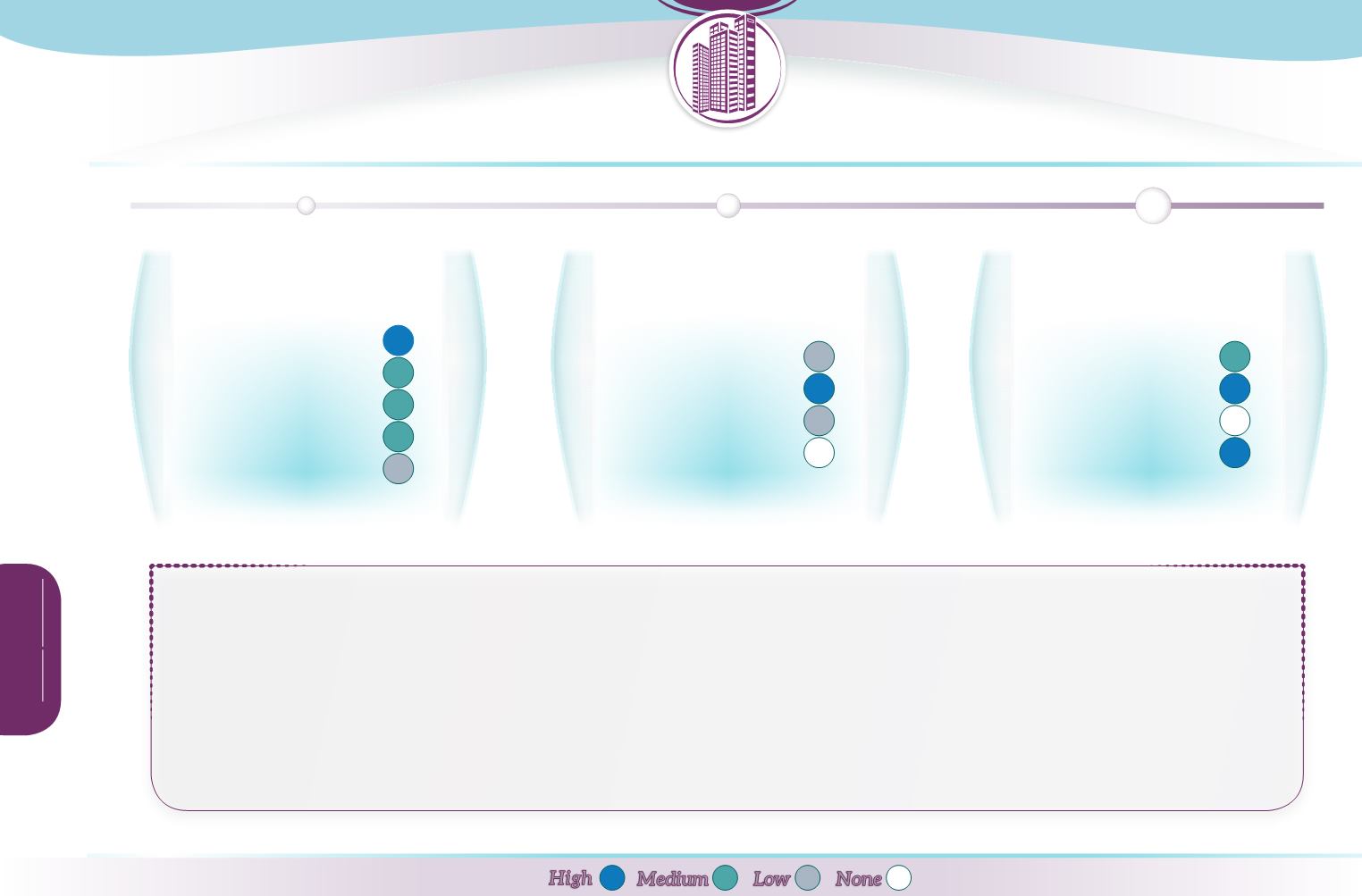
High
Low
Medium
None
Rain gardens are effective at
capturing runoff
from medium sized rainfall events: the use of trees will increase evapotranspiration and the garden can be designed to infiltrate
captured storage, thus reducing runoff. Rain gardens thereby reduce the risk of
flooding
in conjunction with other SuDS features in urban areas, and provide a contribution to
climate change adaptation.
Where infiltration is allowed, rain gardens contribute to
groundwater recharge
, thereby improving groundwater status, although the volume contribution from each rain
garden is small.
Rain gardens can be highly effective at absorbing
hydrocarbons and heavymetals
through vegetative uptake and the composition of soils. They capture sediment, reducing
suspended solid concentrations downstream. Through reducing diffuse pollution, rain gardens make a small contribution to preserving and improving surface
water quality
.
By creating new areas of diverse vegetation, rain gardens contribute to increasing
biodiversity
and providing
aesthetic
benefits in urban landscapes. They may provide some
contribution to lowering peak temperatures and increasing localised uptake of CO2. As a green infrastructure component, particularly where native planting is used, increased
application of rain gardens will contribute to meeting the objectives of the 2020
Biodiversity Strategy.


