E
cosystem
servicesdelivered
Provisioning
Regulation & maintenance
Cultural
Abiotic
C
ontribution
topolicyobjectives
Water Framework Directive
Floods Directive
Birds & Habitats Directive
2020 Biodiversity Strategy
P
otential
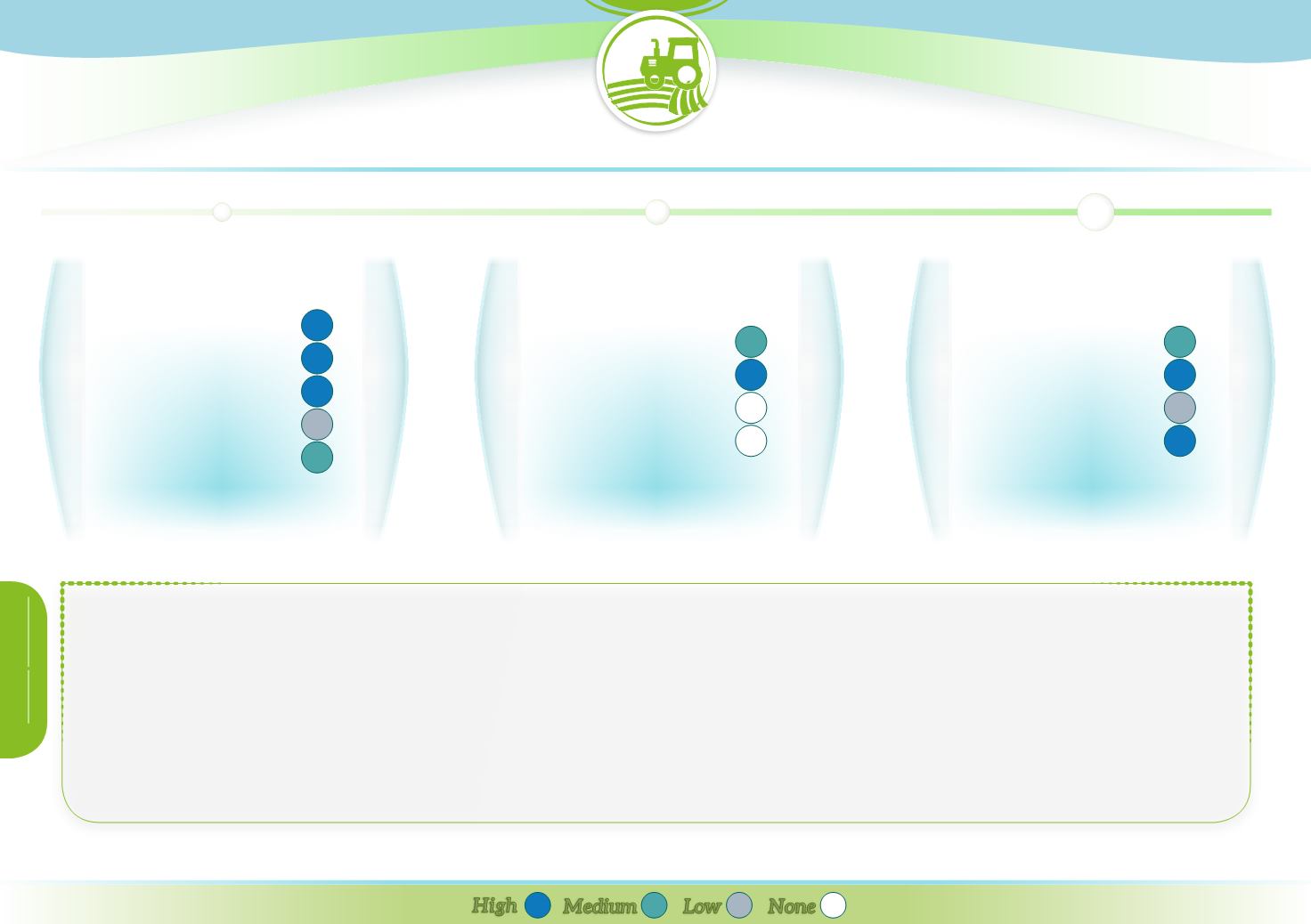
biophysicaleffects
Runoff
Reducing pollution
Soil conservation
Habitat
Climate Change
High
Low
Medium
None
Green cover usually
increases evapotranspiration and infiltration
compared to bare soil, which results in
runoff reduction
(up to 80% or 50mm). In some cases it can
reduce evapotranspiration, thus increase soil water retention, which enhances groundwater recharge. By slowing and reducing runoff, green cover contributes to reduced flood risks,
decreased erosion (up to 50%) and sediments loss (up to 4.2%). Associated with no tillage, it results in between 12 and 46% of
water savings
.
Through uptake from the soil, green cover reduces
pollutant leftovers
(by 10 to 46kgN/ha) and concentration in drainage water (by 23 to 85% for NO3-). Thus it contributes
to preventing surface water deterioration by reducing both pollutant leaching and sediments loss. Enhanced groundwater recharge may help to maintain good groundwater status.
Green cover can catch 300kgC/ha, up to 0.38tN/ha (catch crops) and make nutrients available, improving
soil fertility
. Through taking up carbon, green cover plays a role on
climate change mitigation.
Green cover provides
habitats
and enables maintaining good conditions for further cropping thus contributing to sustainable agriculture. Finally, it may have a positive impact
on the
yield
of following crops (+1 to +75% for legume cover).


