32
Chapter3
Effectivenessof soil conservationpractices forachievingvariouspolicygoals
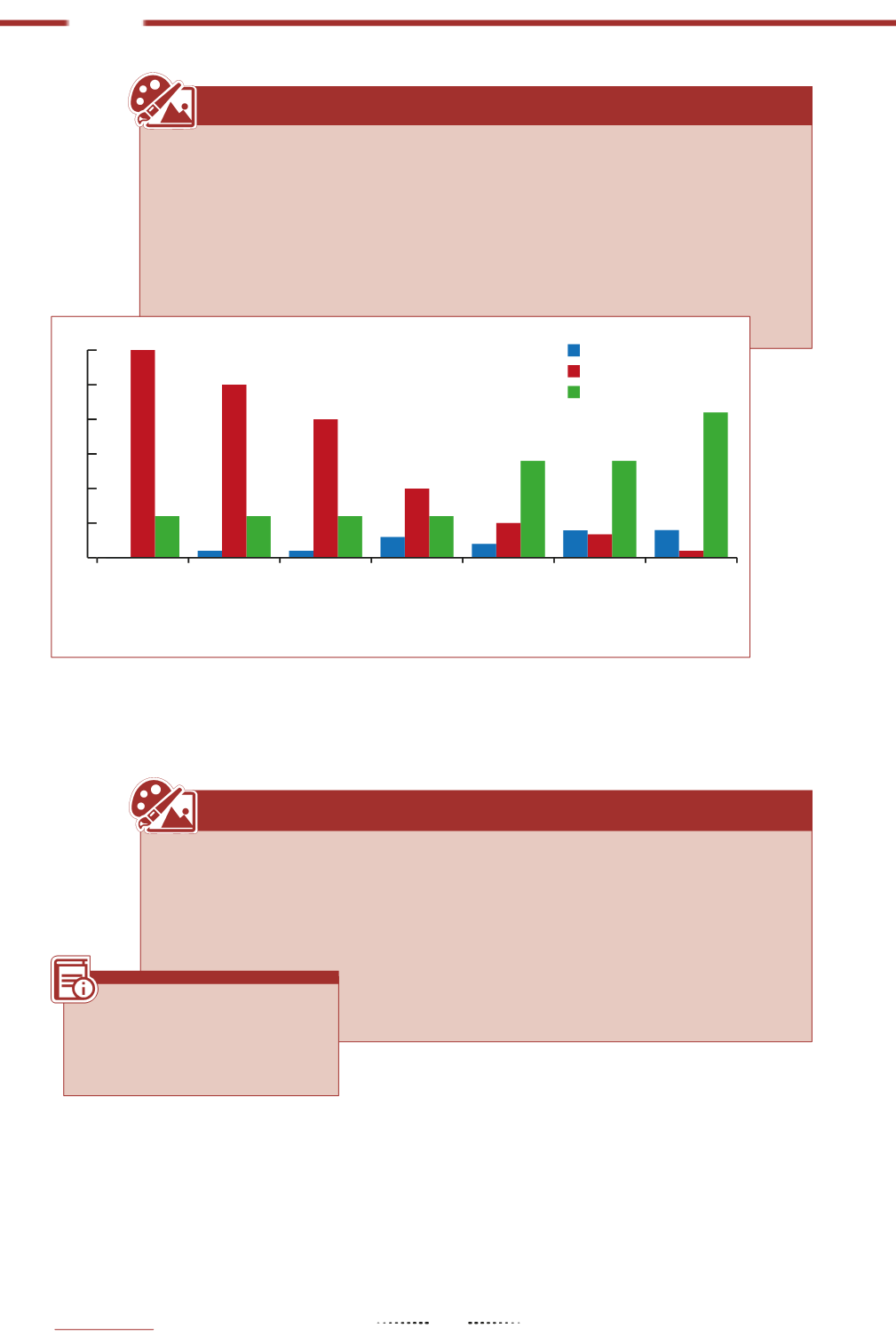
Soil conservationpractices insouthernSpainhavebeenstudiedfor theircontributions tofixing
carbon (Nietoet al., 2010; Smithet al., 2008; Sofoet al., 2005; IPCC, 2003), retaining sediments
(Gómez et al., 2009 and Francia-Martínez et al., 2006) and effectiveness at increasing bird
diversity (Duarte et al., 2010; De la Concha et al., 2007; Muñoz-Cobo et al., 2003). All this
informationhasbeencompiledandcomparedbyRodríguez-Entrenaetal., 2014; (see thefigure
below).However, theexisting literature isuninformativeabout theeffect of themeasuresover
waterbalances.
Illustration7
Bare soil with tillage
and pruning debris
burning
Bare soil with tillage
and incorporation of
shredded pruning
debris
Bare soil with
no tillage
and incorporation of
shredded pruning
debris
Weed cover crops
under herbicide
control and prunir
debris burning
Weed cover crops
under herbicide
control and
incorporation of
shredded pruning
debris
Weed cover crops
under mechanical
control and
incorporation of
shredded pruning
debris
Bare soil with no
tillage and prnnis
debris burning
Carbon Sequestration C0
2
t/ha/year
Erosion Control Soil
Ton/ha/year
Biodiversity (# of bird species)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Source: IMDEA, elaboration based on the above-mentioned references.
GreenRoofs inVienna,Austria: acost-effectivemeasure
Since2003, theCityofViennahas supported the installationof green roofsonflat rooftops in
the cityat a rateof 8-25€/m² (2,200€maximum).A studyon theeconomicefficiencyof green
roofs has shown that the additional costs of installation compared to conventional roofs are
offset by energy savings and the longer lifespanof the roof. For example, Porsche andKöhler
(2003) andHermy et al. (2005) assume that the life span of the roof covering doubles when
a green roof is constructed. Mann (2002) and Saiz et al. (2006)
estimate the life span of green roofs to be between 30 and 50
years.
Illustration8
Learnmore:


