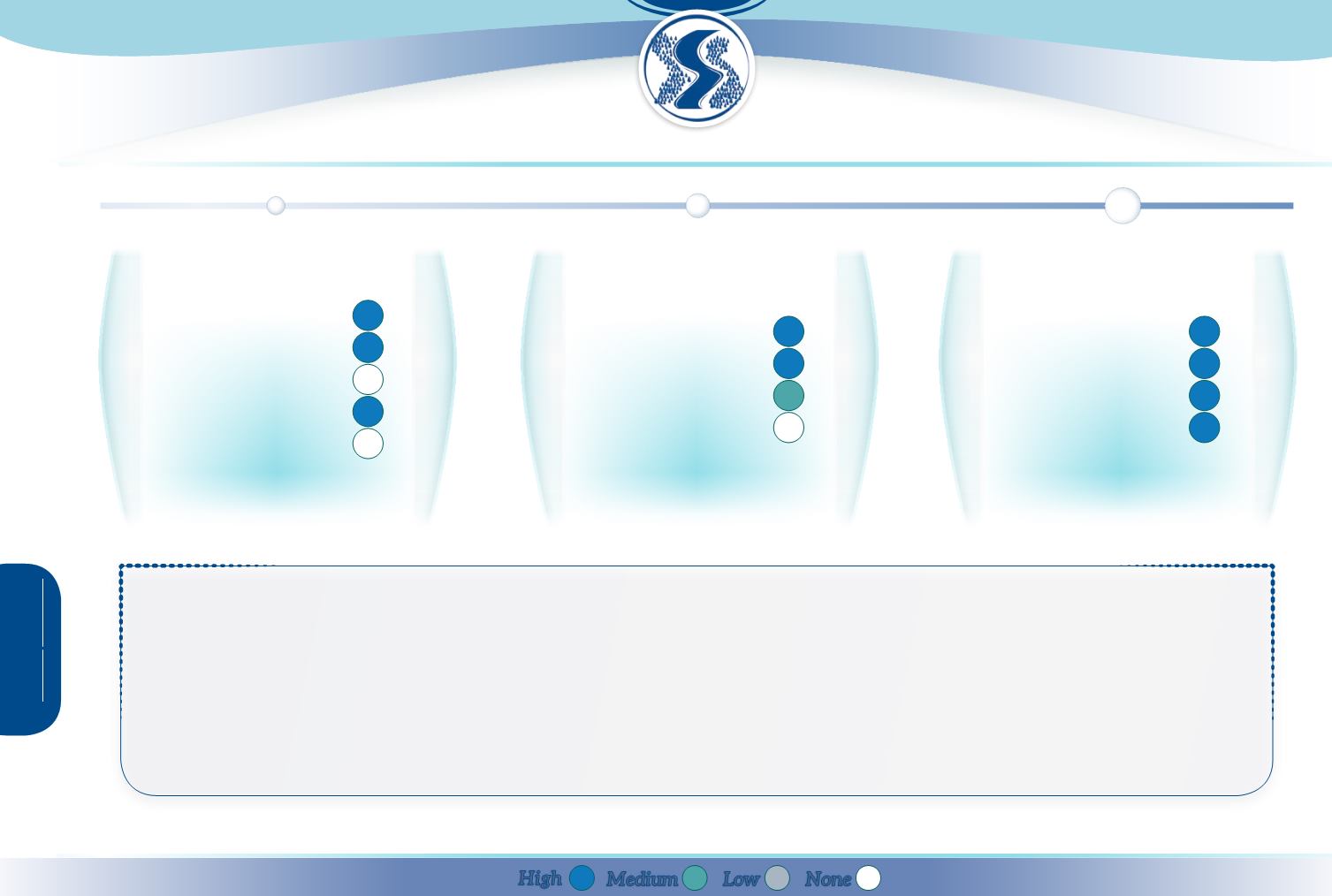
E
cosystem
servicesdelivered
Provisioning
Regulation & maintenance
Cultural
Abiotic
C
ontribution
topolicyobjectives
Water Framework Directive
Floods Directive
Birds & Habitats Directive
2020 Biodiversity Strategy
P
otential
biophysicaleffects
Runoff
Reducing pollution
Soil conservation
Habitat
Climate Change
High
Low
Medium
None
Elimination of riverbank protection restores links between rivers and floodplains, thus improving the capacity of the river to
store water
for long periods. New vegetation and
a wider space for water
slow down
the river flow, reducing peak flows in receiving watercourses, and consequently reducing flood risk and erosion.
Elimination of riverbank protection enhances
sediment and pollutant deposition
in the re-connected reaches and across the floodplain, thus reducing their load in the
river. The combination of biological, chemical and physical processes that occur in floodplains can improve water quality across a wide range of compounds and elements. Reduced
flows also contribute to the filtration of pollutants, potentially improving
surface water qualitative status
and preventing surface and groundwater status deterioration. It
also provides better protection for ecosystems. The continuity between river and floodplain, as well as reduced peak flows, provides benefits to fish species and hence can improve
aquatic ecosystem quality
and fish stocks. Re-opened river banks provide spawning grounds for fish and diversify riparian habitats. More broadly, the measure contributes
to increasing biomass production and preserving biodiversity.
Elimination of riverbank protection also facilitates access to the river, increasing recreational opportunities, and provides aesthetic value compared to artificial infrastructure.


