E
cosystem
servicesdelivered
Provisioning
Regulation & maintenance
Cultural
Abiotic
C
ontribution
topolicyobjectives
Water Framework Directive
Floods Directive
Birds & Habitats Directive
2020 Biodiversity Strategy
P
otential
biophysicaleffects
Runoff
Reducing pollution
Soil conservation
Habitat
Climate Change
High
Low
Medium
None
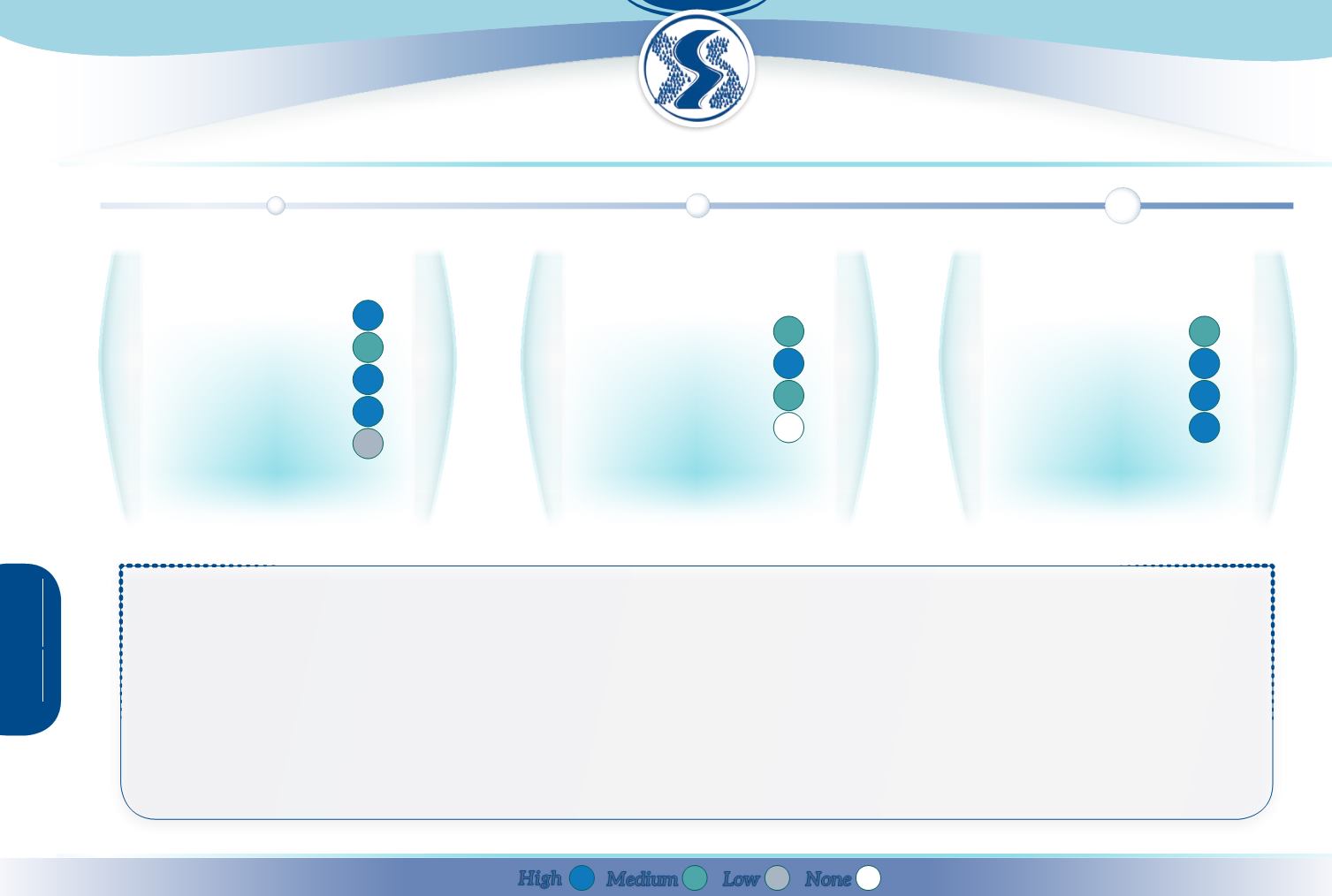
Through increasing the total river length and the interception surface during flood events, reconnection of seasonal streams contributes to
storing
runoff and river water. It
contributes to
slowing river flow
by temporarily diverting a part of the flow to the tributaries. Groundwater recharge in ephemeral stream channels can be increased by their
reconnection to the main river. By storing large quantities of water, limiting flood intensity and playing an essential role in the river basin functioning, restoration and reconnection
of seasonal streams can contribute to
climate change
adaptation.
Headwater streams can intercept nutrients and contaminants before they reach larger perennial streams, depending on the extent of the vegetative cover and soil organic matter
rate on the stream banks. By slowing down the river flow, the measure contributes to
reducing erosion
on the river bed and banks, as well as favouring sediment deposition.
Riparian environments created by ephemeral and intermittent streams, especially when they are reconnected with the main stream, provide structural elements of food, cover,
nesting and breeding habitat, and movement/migration corridors for wildlife. Restoration and reconnection of seasonal streams contributes to the establishment of floral and faunal
species and to avoiding
fragmentation
, therefore preserving
biodiversity
.
The measure can improve the status of hydromorphology, chemical and biology quality elements, and improve groundwater status.


